
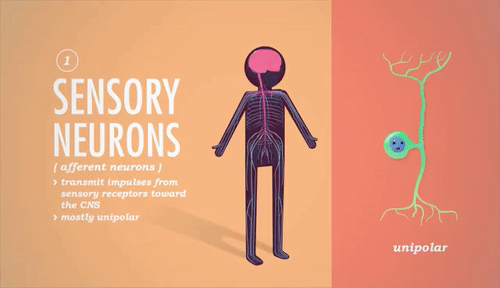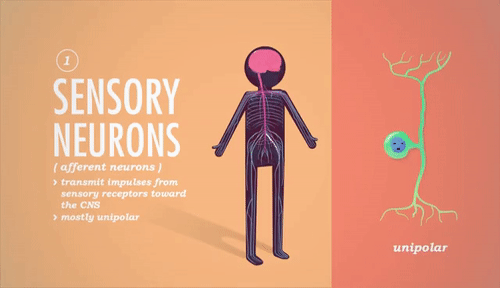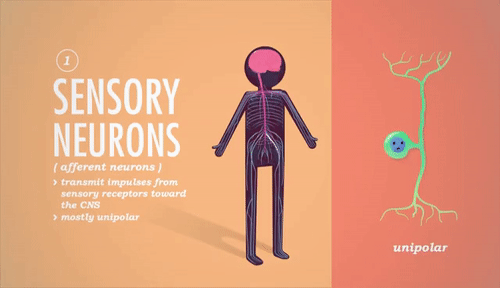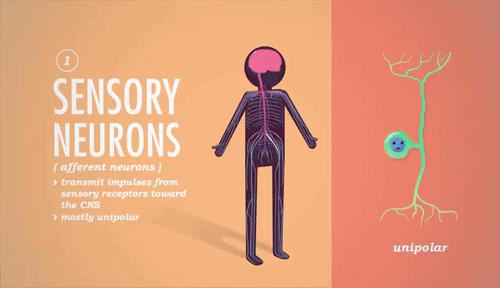

Explain in 4 steps how a spinal reflex arc works.An example is the rapid withdrawal of a paw from a sharp thorn. What is a reflex arc? Can you give an example?Ī fixed, involuntary reaction to a stimulus as a result of a combination of automatic responses to spinal reflexes.Some of the neurons may be inhibitory rather than stimulatory.Name 2 factors that may cause varying effects on the nervous system.What is the name of a junction between a nerve fibre and a muscle fibre?.What is the difference between a somatic motor nerve and a visceral motor nerve?Ī somatic motor nerve takes instructions to the voluntary muscle, whilst a visceral motor nerve takes instructions to the involuntary (smooth or cardiac) muscle.What is the difference between afferent and efferent nerve fibres?Īfferent fibres carry sensory information towards the CNS (motor nerve fibres), whilst efferent fibres carry signals away from the CNS (sensory nerve fibres).What name is given to the organ, muscle or gland where the nerve endings terminate?.What is the name given to a collection of neurons and fibres, forming an independent nerve centre, as is found in the sympathetic nervous system?.Chemical transmitters pass the impulse across the space.Īn impulse can only pass in one direction across a synapse. The termination of an axon with the dendrites of another neuron. Each nerve carries information as an electrical impulse. Many neurons (see Q5) bound together in a connective tissue sheath. Briefly describe the structure and function of a nerve.Multipolar - a neuron having connections with many cells.Bipolar - a neuron having connections with 2 cells.Unipolar - a neuron having a connection with only one cell.What is meant by the following: unipolar, bipolar and multipolar?.This fatty substance allows nervous impulses to travel more rapidly. Some axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath.Nerve endings - which transmit the nervous impulse to the dendrites of the next axon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
